Corporate Governance
Risk Management
Enterprise Risk Management is an integrated, structured, and cultural process, and activity implemented by SIG, aimed at both realizing potential opportunities and managing adverse impacts on the Company. SIG has consistently applied risk management since 2005, integrating it into all business processes and using it as a key consideration in making strategic and operational decisions. Effective and consistent risk management within the company allows SIG to seize opportunities, anticipate changes in a dynamic business environment, and maintain investor confidence.
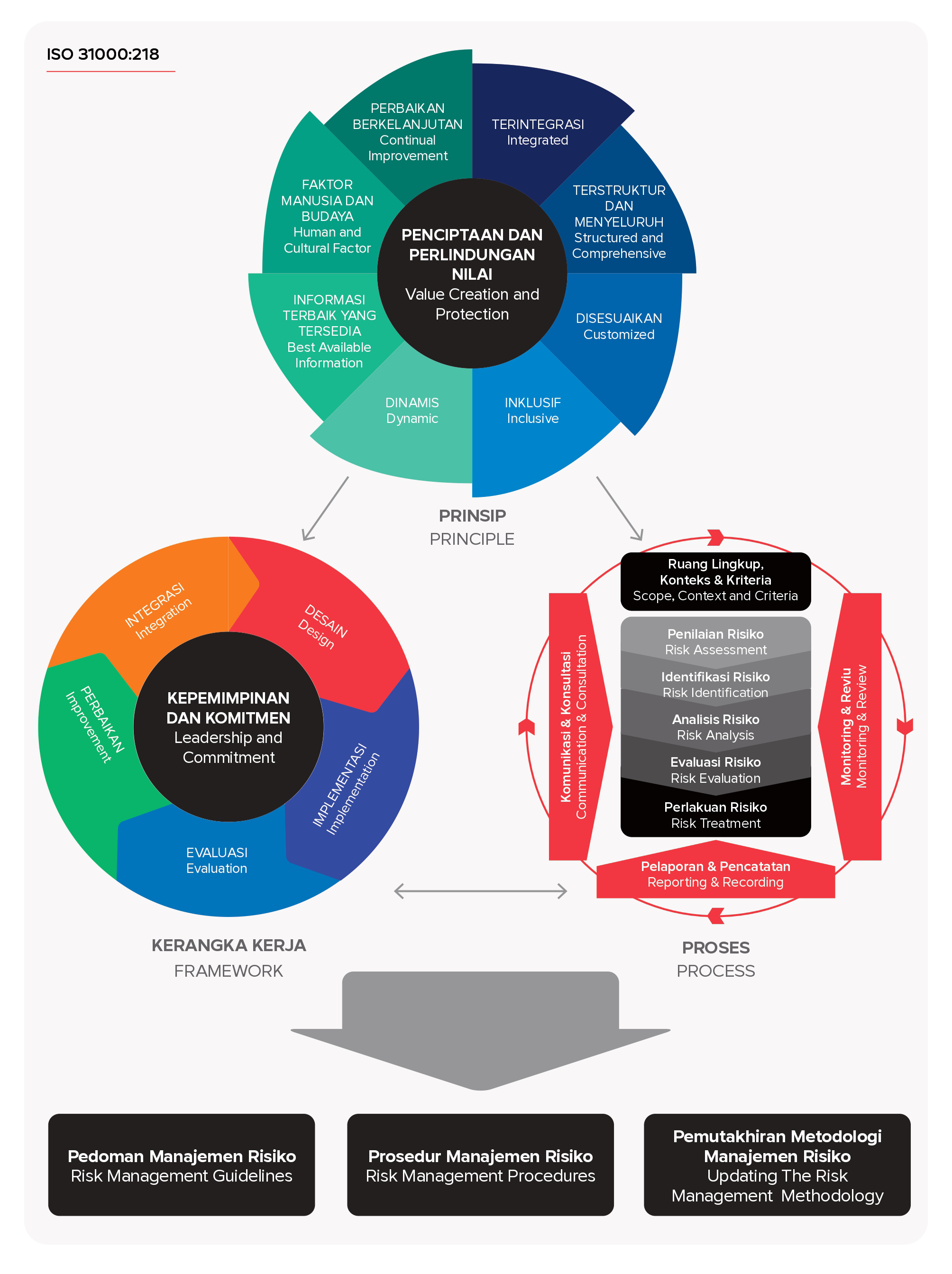
SIG’s Risk Management is based on ISO 31000:2018 and refers to the Ministry of SOEs Regulation No. PER-02/MBU/03/2023, concerning Guidelines for Governance and Significant Corporate Activities of State-owned Enterprises (“PERMEN 02 Year 2023”), ratified as of 17 April 2023, which comprises Principles, Framework, and Risk Management Processes.
The Implementation of Risk Management is then standardized in the Risk Management Guidelines and Risk Management Procedures.
SIG’s risk management process is supported by the risiko.sig.id application, which continues to evolve and adapt to deliver sustained added value to the Company. The risiko.sig.id application functions as a tool for managing corporate and operational risks and can issue alerts to the Risk Taking Unit. This facilitates the compilation of a Risk Register and regular reporting of progress in Risk Control and Mitigation. This facilitates the Enterprise Risk Officer in monitoring the implementation of the risk management process within the company.
SIG’s risk management is embedded and integrated into the Company’s management systems, business activities, and decision-making processes. It plays a crucial role in formulating strategies, long-term plans, and the company’s work plans and budget. Risk management is also a regular topic of discussion in meetings of the Board of Directors and the Board of Commissioners.
The risk culture program is consistently executed through:
- Training and certification programs for Risk Management Body;
- Assistance to Risk-Taking Unit Officers in compiling risk registers;
- Risk awareness campaign;
- Risk and safety briefings; dan
- The implementation of drills, tests, and simulations in response to crisis conditions;
The risk culture program is consistently implemented to enhance understanding and awareness of risk management across all internal and external elements of the Company. This ensures that risk management is an integral part of the Company’s business processes. Moreover, the program emphasizes that “risk is everyone’s responsibility,” fostering a collective responsibility for managing risks effectively.
RISK MANAGEMENT ORGANIZATION AND GOVERNANCE

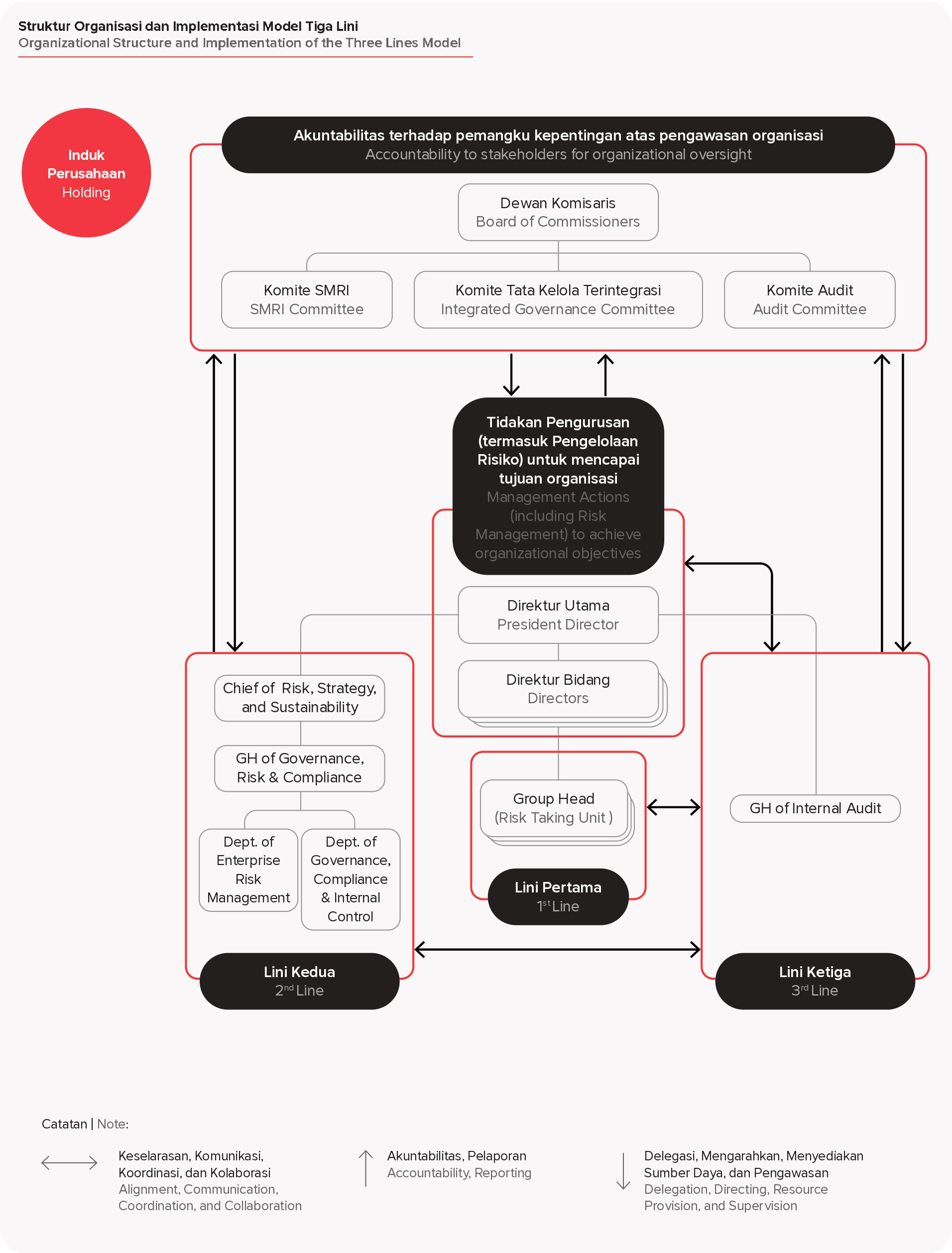
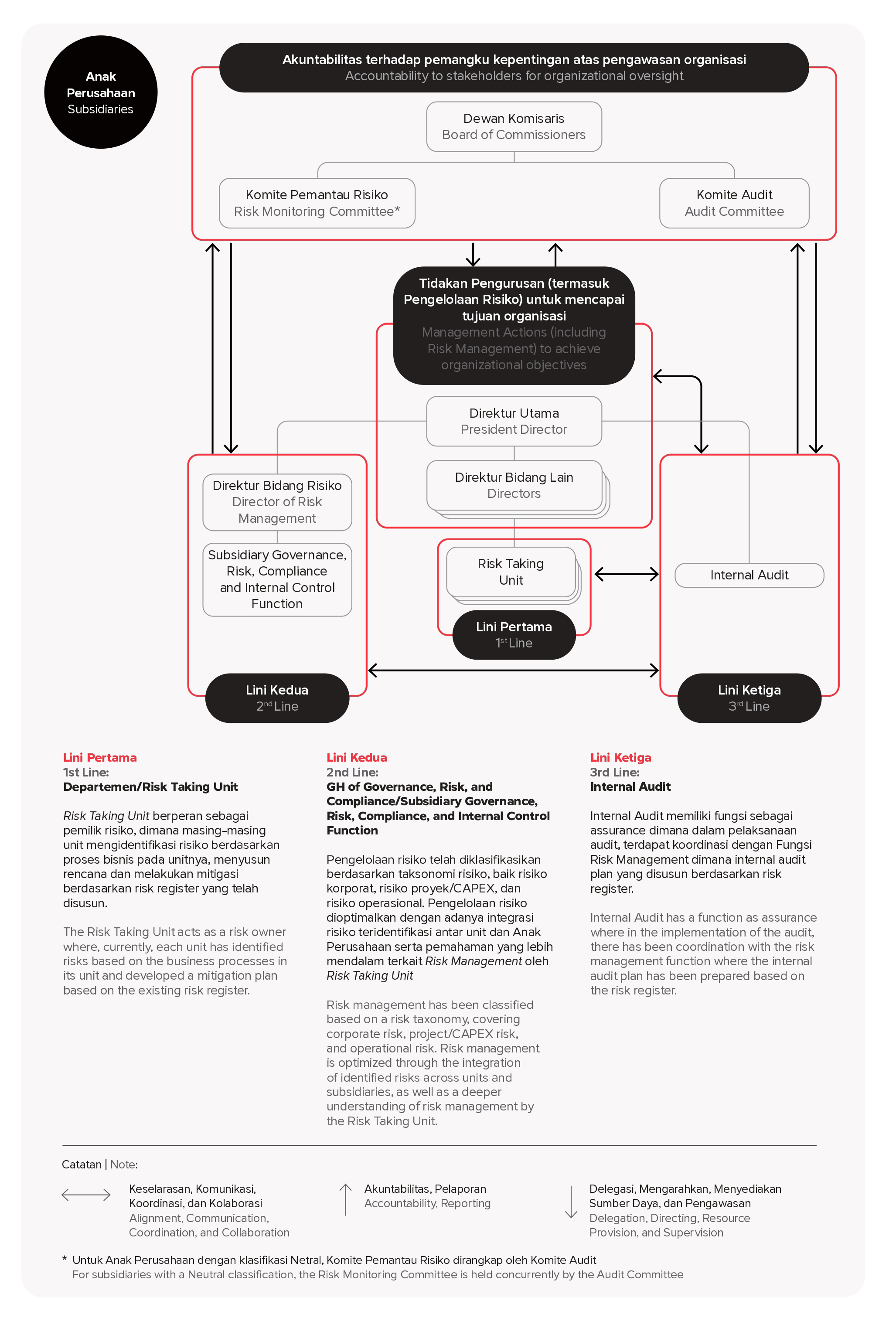
SIG, as a Systemic A and Conglomerate SoE, has implemented a risk management governance framework that encompasses all of the Company’s business processes, following the Three Lines Model (3LM) as outlined in PERMEN 02 of 2023. This model helps to distinguish the roles and functions of each line.
The first Line consists of the Risk Owner Unit, which directly identifies and manages risks in business processes. The second line involves the Independent Risk Management and Compliance Functions, which monitor risks at an aggregate level and develop the Company’s risk management methodologies and policies. The third line is the Internal Audit Function, which ensures that governance and risk controls are effectively implemented across the company.
To enhance the qualifications of the Company’s Risk Management Body, the Company conducts certification and training programs for personnel, including the Board of Commissioners, Directors, Audit Committee, Risk Management Committee, Integrated Governance Committee, Risk Management Unit, Internal Audit, and Risk Owner Units in the areas of risk management, good governance, and compliance management in accordance with PERMEN 02 of 2023.
EVALUATION OF RISK MANAGEMENT IMPLEMENTATION

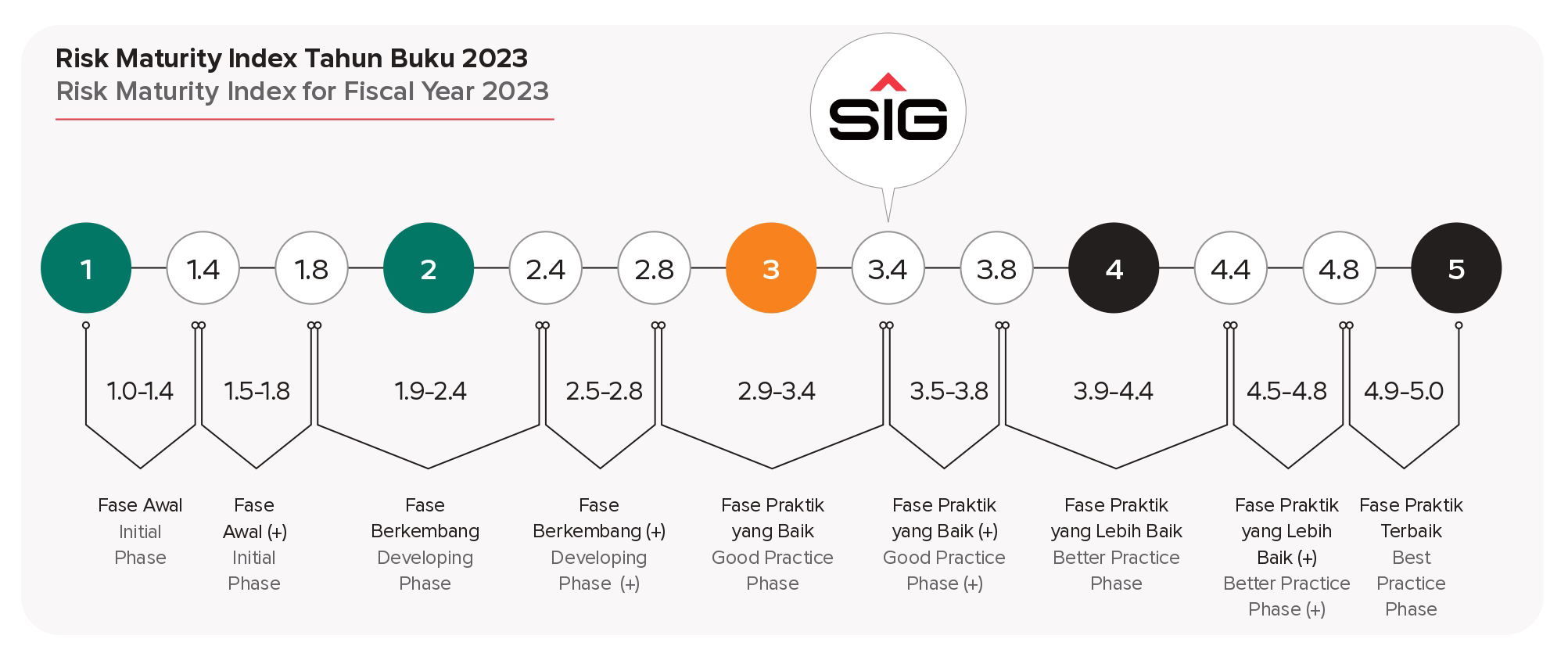
In 2024, SIG assessed the quality level of the design and effectiveness of its Risk Management implementation in protecting and creating value, based on Regulation of the Minister of SOEs 02 of 2023 for the fiscal year 2023, conducted by an independent party.
The Risk Maturity Index assessment is performancebased, combining the dimensional aspect and the company’s performance achievement aspect, as reflected in the final health rating level and composite risk rating. The composite risk rating is used to measure the effectiveness of corporate risk management, operational performance management, and financial performance management within the Company.
SIG achieved a final Risk Maturity Index score of 3.4 out of a scale of 5, with the rating of Good Practice Phase.
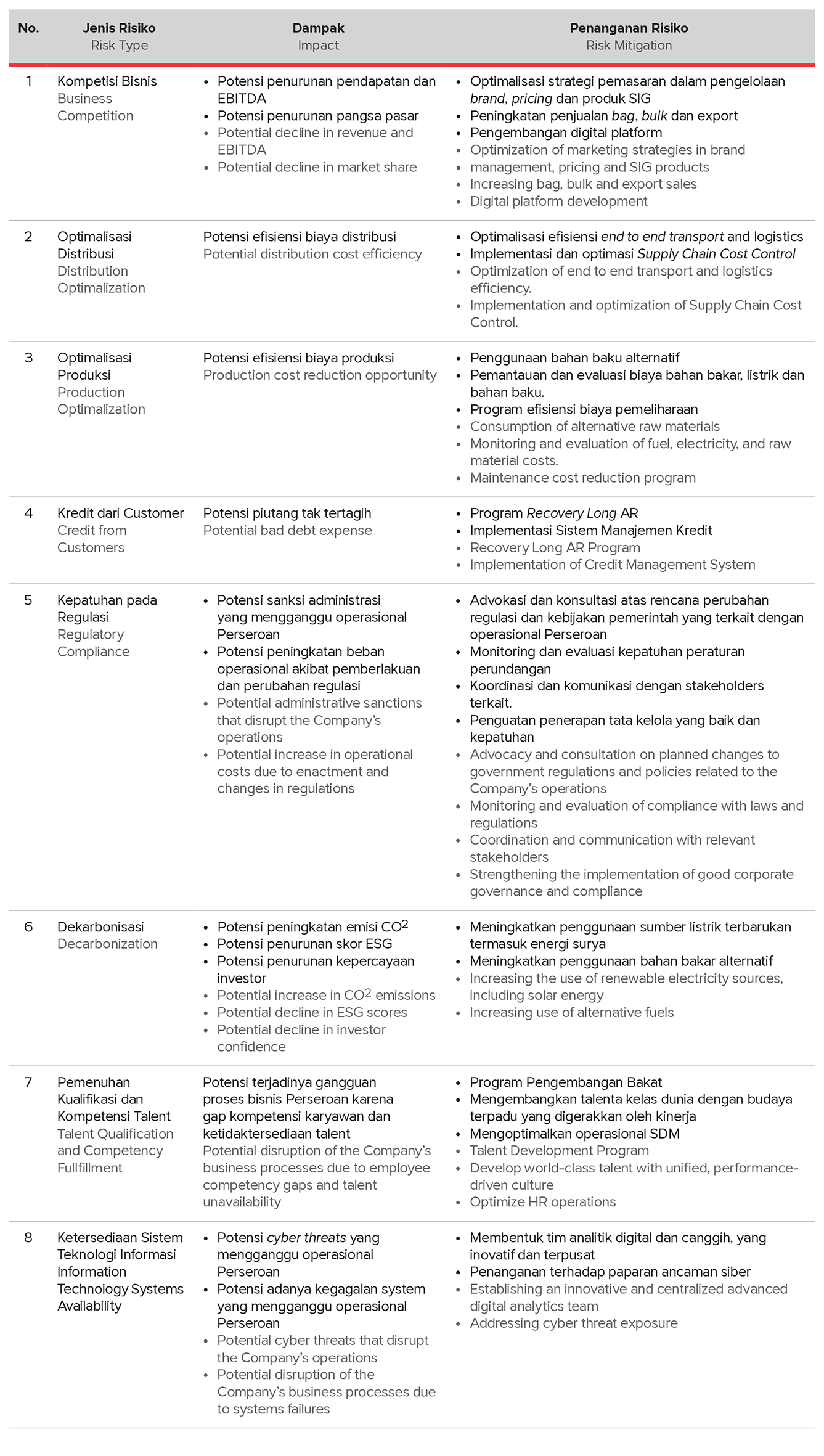
CORPORATE RISK 2024

SIG conducts annual risk assessments, considering internal and external factors that may affect the Company’s long-term plans, targets and performance. SIG has also established risk treatment measures to minimize the impact and likelihood of risks to the Company, resulting in the following SIG risk profile for 2024:
BUSINESS CONTINUITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (BCMS)

As a publicly listed company in a strategic industry, SIG plays a crucial role in supporting national development and ensuring the continuity of cement supply. To address complex business challenges, SIG has implemented the BCMS as an integrated system for managing risks and ensuring operational sustainability.
SIG BCMS Policy
As part of its commitment to operational sustainability, SIG has established the following BCMS policy:
“Managing business continuity to ensure the continued production of goods and services at predetermined capacity during disruptions, while striving to enhance the Company’s resilience.”
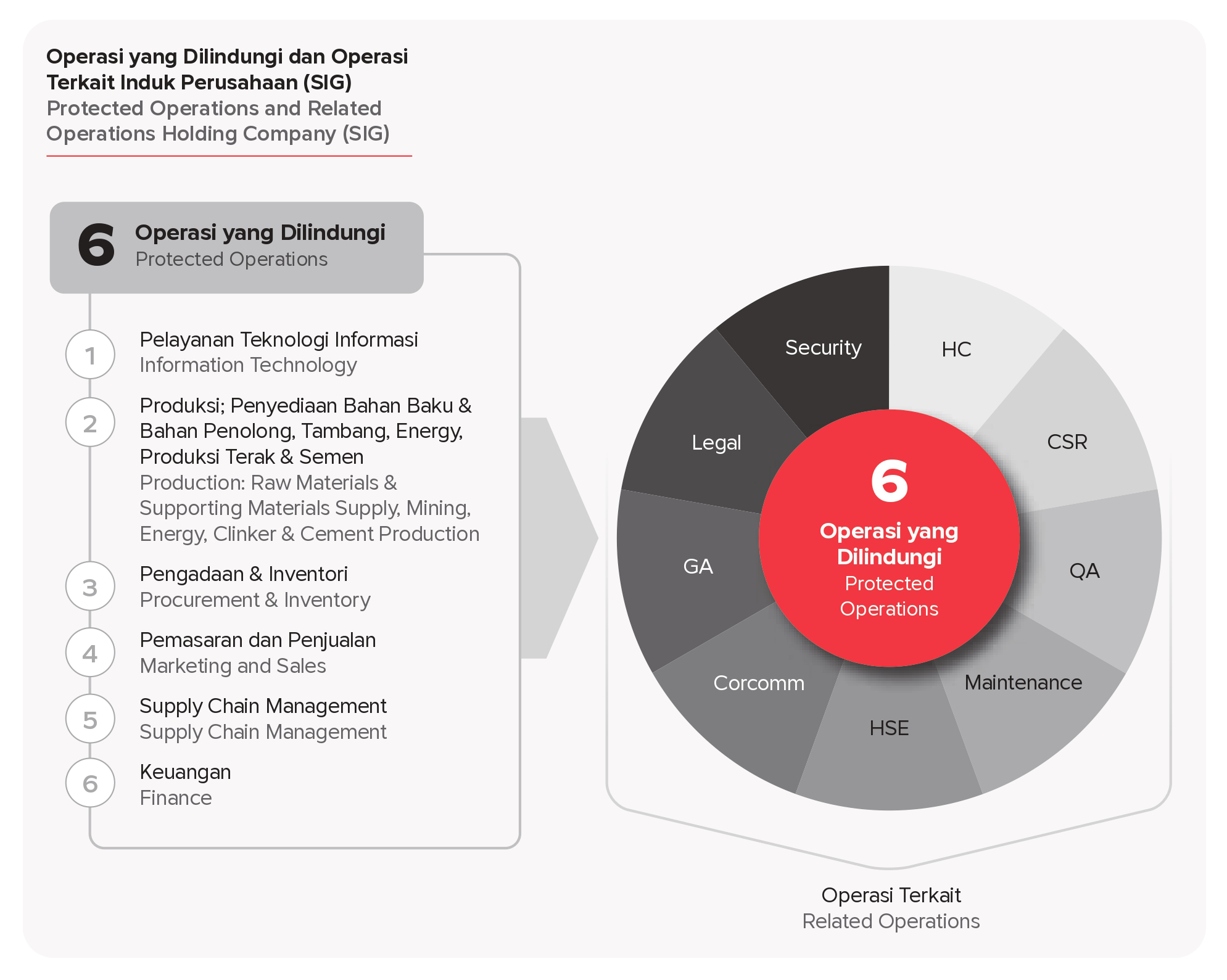
Aligned with the ISO 22301:2019 standard, the implementation of BCMS has been executed from 2022
to 2024, covering six main operations and nine related operations classified under Critical Business Functions (CBF). This system ensures the company’s readiness to respond to disruptions and enhances business resilience.
BCMS Framework at SIG
SIG implements BCMS based on a systematic approach that includes the following steps:
- Risk Identification and Impact Analysis (BIA). Identifying the most critical operational processes and assessing the potential impact of disruptions.
- Sustainability Strategy Development. Developing risk mitigation measures and recovery strategies.
- Response and Recovery Planning. Developing an Emergency Response Plan and Recovery Plan, as well as establishing an emergency response team.
- Training and Testing. Conducting disruption simulations and ensuring operational readiness.
- Monitoring and Evaluation. Performing regular audits and systematic improvements to enhance BCMS effectiveness.
- Communication and Stakeholder Engagement. Actively coordinating to ensure the successful implementation of BCMS.
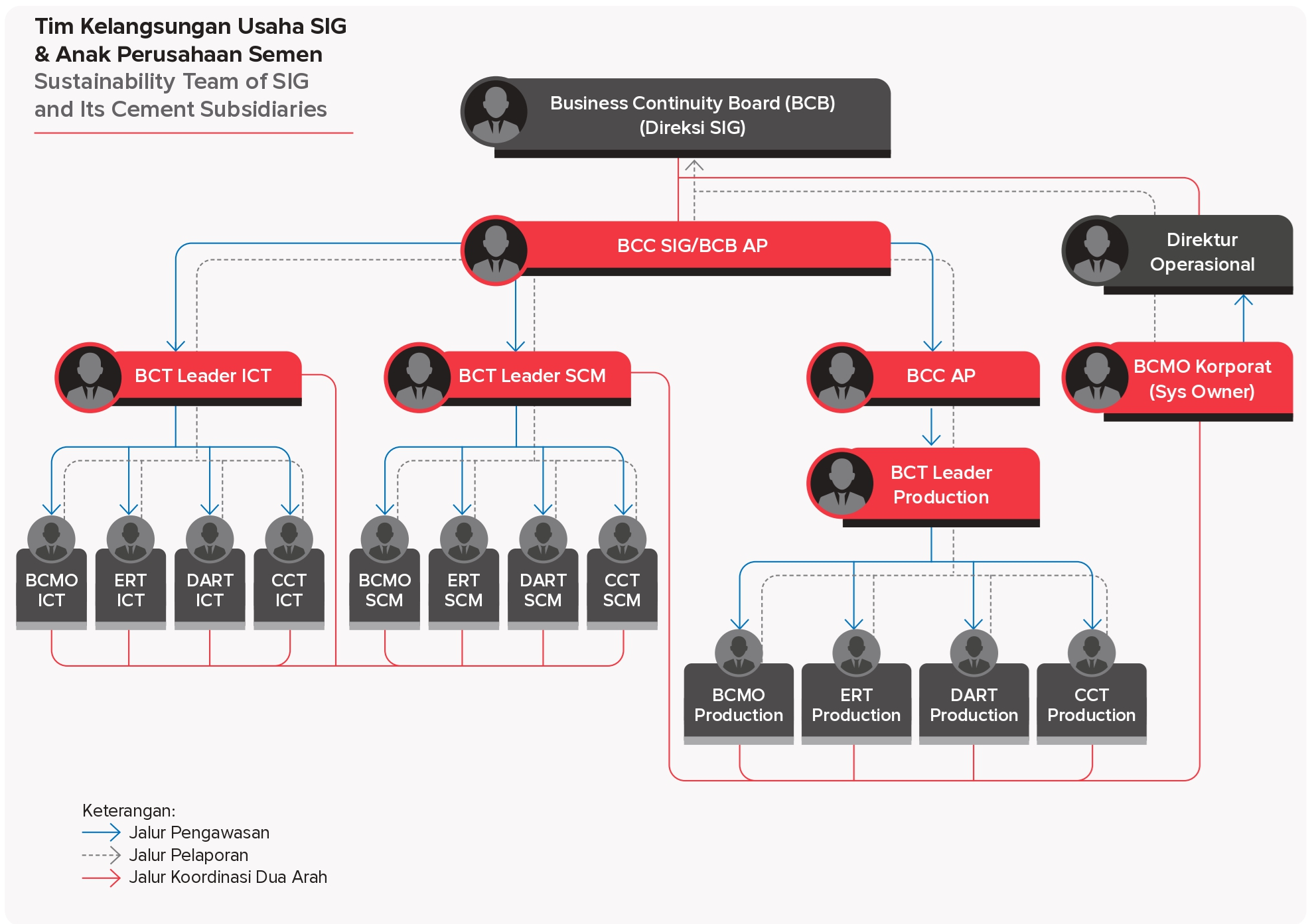
SIG initiated the implementation of the BCMS by securing full support from management, forming a cross-functional team, and conducting business process mapping to identify critical functions that require priority protection.
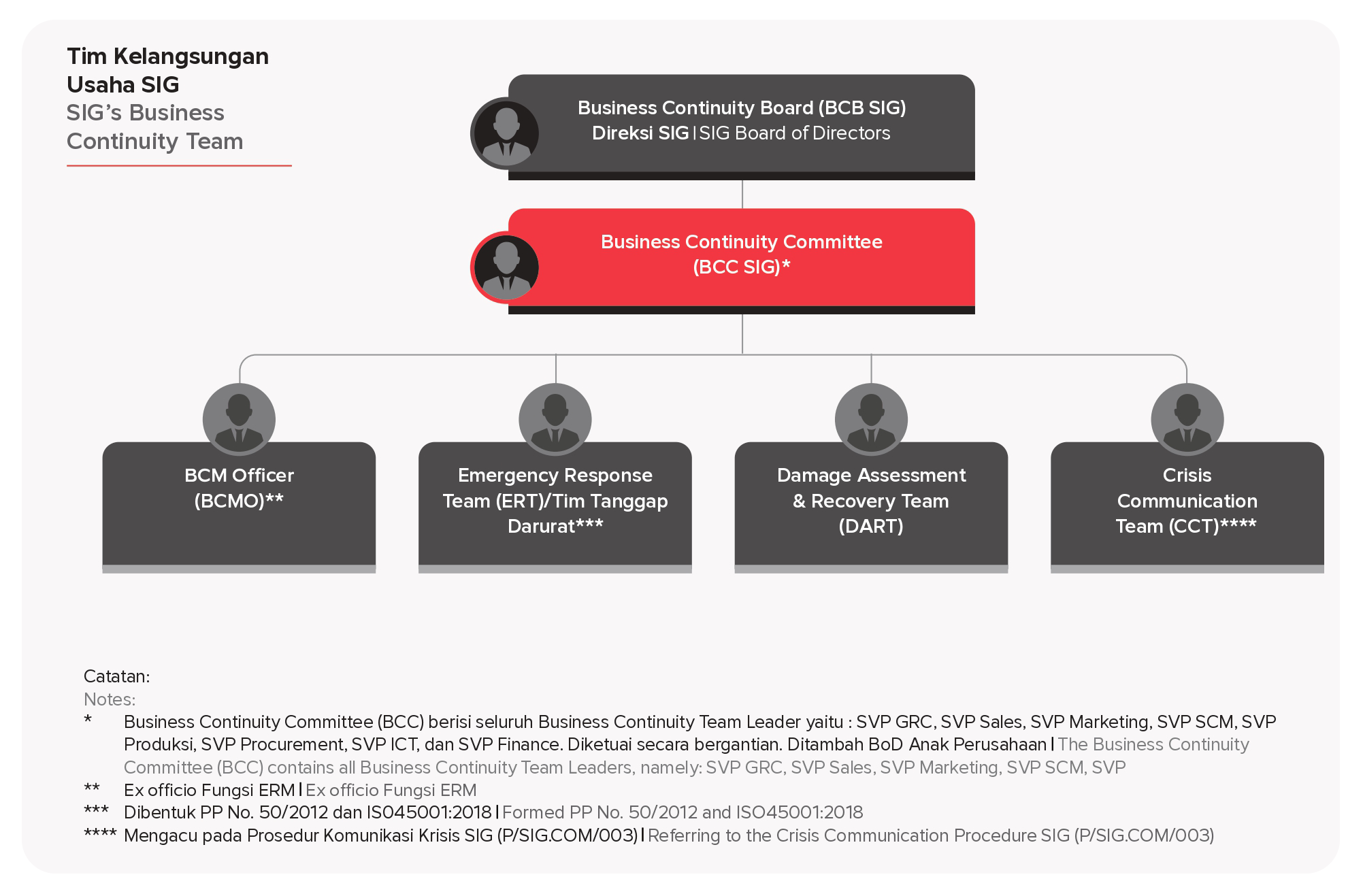
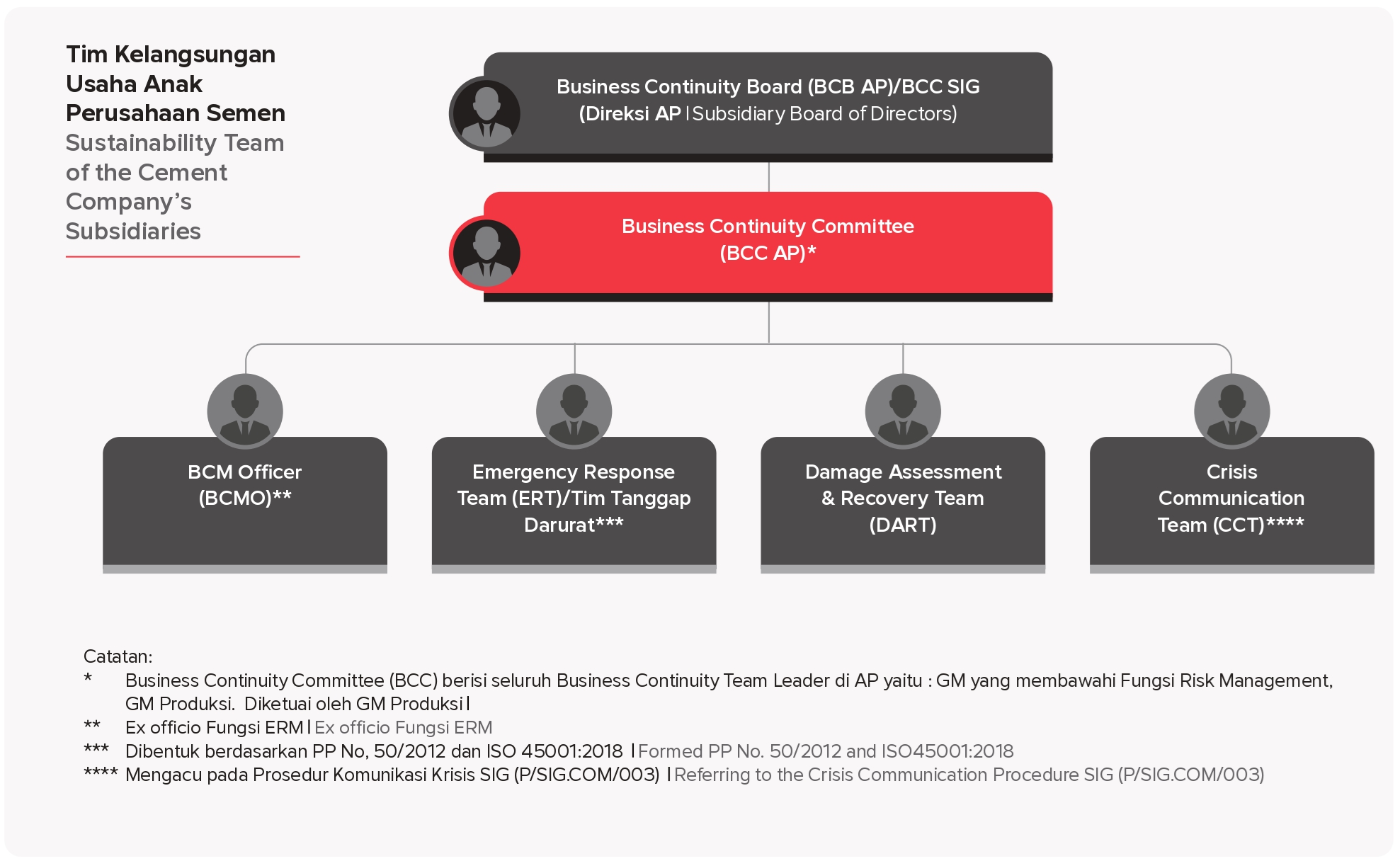
The relationship between the Business Continuity Team at the Holding (SIG) and its Subsidiaries is as follows:
Future Commitment
SIG is committed to continuously enhancing its BCMS through:
- Technology Advancement and Digitalization. Leveraging technology for risk analysis and accelerating recovery processes.
- BCMS Policy Enhancement. Evaluating policies to ensure relevance and effectiveness.
- Collaboration with Partners and Industry. Strengthening synergy with the government and stakeholders.
- Employee Education and Awareness. Providing training to enhance understanding of business sustainability.
Synergy with Sustainability Programs
As part of its sustainability strategy, SIG’s BCMS supports:
- The achievement of the SDGs, particularly SDG 9 (Industry and Innovation) and SDG 13 (Climate Action).
- Energy efficiency and environmental impact reduction in responding to disruptions.
- Community engagement in building a more resilient environment.
IT Governance within the BCMS Framework
SIG has an integrated IT governance within the BCMS implementation. This governance is designed to ensure that the main risks associated with information technology are managed effectively, including:
- Disruption Risk Management. IT system disruption risks are identified through an ISO 31000-based risk assessment process, including risk mapping to critical IT infrastructure such as servers, networks, and critical applications.
- Cybersecurity. The company adopts a layered approach in cybersecurity management, including monitoring for external threats, regular penetration testing, and employee training on cybersecurity threats such as phishing and ransomware, as well as Personal Data Protection (PDP).
- Disaster Recovery. The Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP) is designed to restore critical IT services within a predetermined timeframe specified in the Recovery Time Objective (RTO). The DRP is tested regularly through simulations to ensure its effectiveness.
SIG has implemented specific measures to ensure full integration through:
- Data Backup Management A reliable data backup system ensures that the company’s operational data can be quickly restored.
- Availability of IT Infrastructure Critical IT infrastructure, including servers and networks, is designed with redundancy to minimize the risk of downtime. Currently, SIG has also adopted cloud-based servers and storage for critical applications.
- IT Continuity Simulation BCMS simulations involve IT disruption scenarios, including cyber-attack scenarios and system failures, to test the organization’s readiness in responding to such disruptions..
Results and Impact of BCMS Implementation
Through structured implementation of the BCMS, the Company has:
- Enhanced its readiness to manage operational disruptions.
- Minimized the risk of financial and reputational loss due to interruptions.
- Ensured operational continuity and protection of the interests of customers, employees, and shareholders.
STATEMENT OF THE BOARD OF DIRECTORS AND/OR BOARD OF COMMISSIONERS ON THE ADEQUACY OF THE RISK MANAGEMENT SYSTEM

As a demonstration of the Board of Directors’ commitment to ensuring the adequacy of the risk management system, the Board established Risk Management Guidelines and Procedures based on the international standard ISO 31000:2018 and Regulation of the Minister of SOEs No. 02 of 2023 as a commitment and guideline serve as commitments and guidelines for implementing risk management within the SIG Group. The Board of Directors regularly monitors and evaluates the Company’s risk profile and the implementation of risk management within the Company.
The Board of Directors actively integrates risk management into the Company’s business processes by considering risks in strategic and operational decisionmaking.
The Board of Commissioners, together with the Strategy, Risk Management, and Investment Committee, the Integrated Governance Committee, and the Board of Directors, conducts oversight, provides input, and offers direction on the implementation of risk management to ensure its adequacy.
Based on the results of monitoring and evaluation, as well as reviews conducted by the Audit Committee, Internal Audit, and Independent Auditors, the Board of Commissioners and Management affirm that the risk management system has been consistently and adequately implemented by all stakeholders in managing the Company’s risks






